25 August, 2025
0 Comments
1 category
The benefits of the Sun and Melanin.
Exposure to sunlight is vital for producing vitamin D and regulating mood, while melanin provides natural protection against UV radiation
. The relationship between the two requires a balance: the body uses sunlight to produce beneficial hormones and vitamins, and melanin defends against potential harm caused by overexposure.
Benefits of sun exposure
- Boosts vitamin D production: The body creates vitamin D from cholesterol when the skin is exposed to UVB radiation from the sun. Vitamin D is crucial for absorbing calcium to support bone health and immune function.
- Improves mood: Sunlight increases the brain’s production of serotonin, a hormone linked to feelings of calm, focus, and happiness. This is why many people experience mood improvements on sunny days and may suffer from seasonal affective disorder (SAD) with less sun.
- Regulates sleep: Exposure to natural light during the day helps regulate your circadian rhythm, or internal body clock. This promotes better sleep at night by influencing the body’s melatonin production.
- May lower blood pressure: Research suggests that sunlight exposure can increase nitric oxide levels in the skin, which causes blood vessels to widen and may lead to a modest reduction in blood pressure.
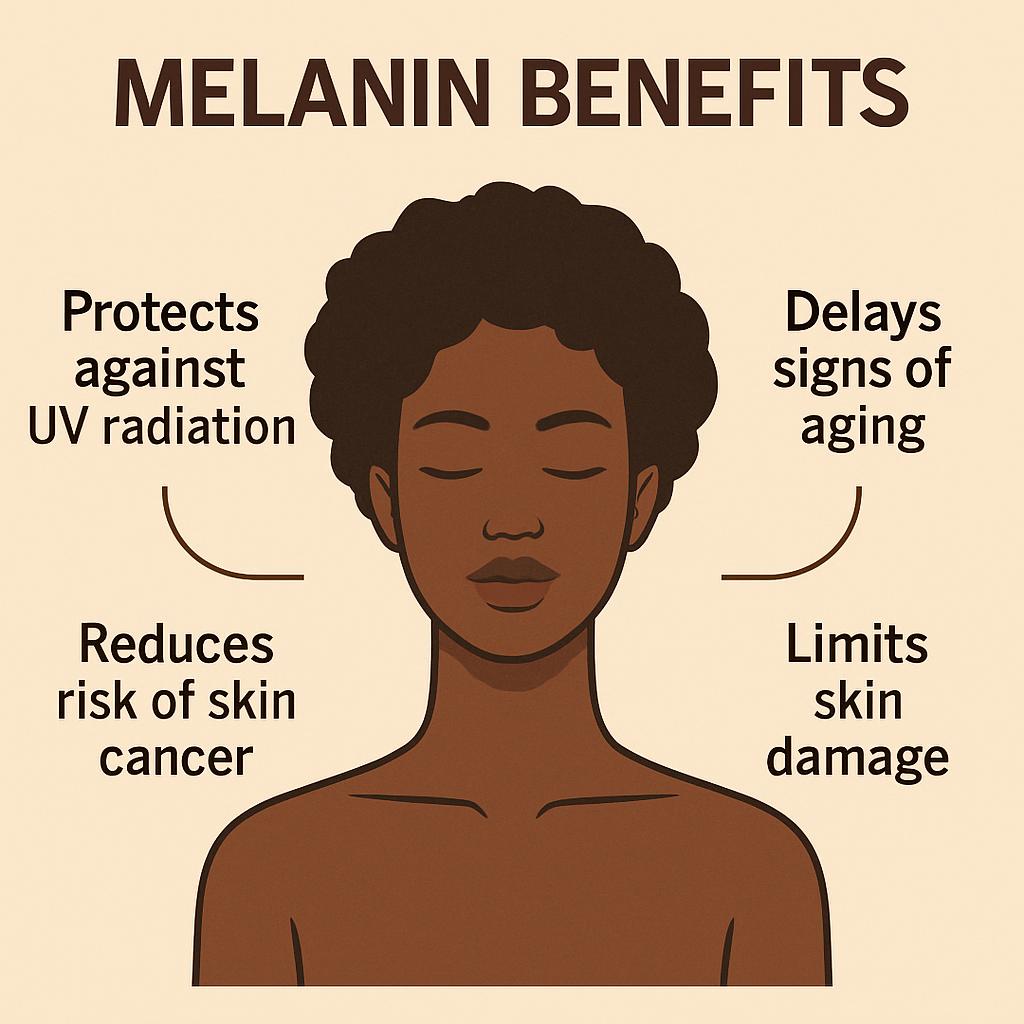
Benefits of melanin
- Acts as a natural sunscreen: Melanin, the pigment that gives skin, hair, and eyes their color, absorbs and scatters harmful UVA, UVB, and UVC radiation. People with darker skin have more melanin (specifically eumelanin), which provides a higher degree of natural photoprotection.
- Protects cellular DNA: By absorbing UV rays, melanin shields the nucleus of skin cells, helping to prevent DNA damage that can lead to skin cancer and premature aging.
- Neutralizes free radicals: Melanin has antioxidant properties that help combat reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are created by sun exposure, pollution, and stress. By scavenging these free radicals, melanin reduces oxidative stress and cellular damage.
- Supports overall skin health: Beyond sun protection, melanin may contribute to immune system support and help reduce inflammation, though more research is needed.
The relationship between sun exposure and melanin
The benefits of sun exposure and melanin are interconnected but require a balanced approach:
- Risk of overexposure: While melanin offers protection, it does not provide complete immunity from UV damage. Overexposure to the sun can overwhelm melanin’s protective capacity, leading to sunburn and increasing the risk of skin cancer.
- Melanin and vitamin D synthesis: Higher levels of melanin act as a stronger filter for UV rays, which can make it more difficult for people with darker skin tones to produce vitamin D. Individuals with darker skin may need longer periods of sun exposure to produce the same amount of vitamin D as someone with lighter skin.
- Need for balance: Regardless of skin tone, experts recommend moderate sun exposure to gain benefits like vitamin D synthesis and mood enhancement. However, this should always be combined with proper sun safety practices like wearing sunscreen and protective clothing to mitigate the risks of excessive UV radiation.
- the sun health benefits arthritis aches covid cancer
- Moderate sun exposure offers benefits for various health conditions, including arthritis, cancer, and COVID-19, primarily through the production of vitamin D and other physiological effects. However, excessive sun exposure is the primary cause of skin cancer and can be dangerous.
- Arthritis
- Warm, sunny weather and sunlight may help reduce aches and pain from arthritis, but excessive exposure can be risky, especially with certain medications.
- Osteoarthritis: Individuals with osteoarthritis often experience reduced stiffness and pain in warm weather. The heat can increase blood flow to the joints and improve flexibility.
- Inflammatory arthritis: While some patients report relief, others with inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid or psoriatic arthritis may find heat and humidity exacerbate joint swelling and discomfort.
- Psoriatic arthritis: For people with psoriatic arthritis and the associated skin condition psoriasis, UV light exposure can improve plaques on the skin.
- Role of Vitamin D: Adequate vitamin D, which is produced by sun exposure, is important for bone health and may help prevent the progression of osteoarthritis. Studies also suggest that sufficient sun exposure may lower the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis.
- Cancer
- Sunlight’s relationship with cancer is complex: it can cause skin cancer, but it may also offer protective benefits against other types of cancer.
- Skin cancer risk: Excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is the primary cause of skin cancers, including melanoma and non-melanoma types. Sunburns, especially during childhood, significantly increase the risk of melanoma.
- Other cancers: People who live in sunnier areas with more daylight hours are less likely to have certain types of cancer, including colon, breast, prostate, and Hodgkin’s lymphoma. This protective effect is partially attributed to vitamin D synthesis but also involves other sunlight-activated mechanisms.
- Vitamin D’s protective role: Adequate vitamin D is crucial for cellular regulation and has shown potential in reducing the risk of developing certain cancers.
- COVID-19
- Research conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic suggested a link between sunlight exposure and outcomes, though it is not a treatment for the disease.
- Reduced mortality: Observational studies found that populations in sunnier areas with higher UV exposure had lower COVID-19 mortality rates, independent of vitamin D levels.
- Inactivation of the virus: Laboratory studies have shown that simulated sunlight can inactivate the SARS-CoV-2 virus, though this effect is not a substitute for proper public health measures.
- Role of nitric oxide: Researchers speculate that sun exposure causes the skin to release nitric oxide, which may reduce the ability of the virus to replicate.
- Important safety considerations
- To balance the benefits and risks of sun exposure, health experts recommend following sun safety guidelines:
- Use sun protection: Wear a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, protective clothing, and a wide-brimmed hat.
- Seek shade: Avoid direct sunlight during the strongest hours, typically 10 a.m. to 4 p.m..
- Moderation is key: Get limited, non-burning sun exposure to help your body produce adequate vitamin D while minimizing the risk of skin cancer.
- Consider supplements: If you have concerns about getting enough vitamin D from the sun, consider supplementation and speak with a healthcare professional.
Category: Health & Well Being


